Toshiba memory is rebranded to Kioxia, going forward.Kioxia Exceria
This particular brand is owned by Toshiba right ? Or was ? I remember the time when I was looking for it back when I was building PC more often
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
SONY NW-WM1Z M2 / WM1A M2
- Joined
- Oct 14, 2013
- Posts
- 28,361
- Likes
- 32,235
Nice!! If someone would take a chance and order 1TB to compare for sound quality, I would like to know for sureToshiba memory is rebranded to Kioxia, going forward.
I have a Kioxia Exceria High Endurance 256GB. Also a Micron MTSD256AKC7MS-1WT, which is the series before the current i400 that many people say is much better.Nice!! If someone would take a chance and order 1TB to compare for sound quality, I would like to know for sure
I rated the Exceria higher than the Micron, though at that time, the Micron was more than double the cost of the Exceria.
The Sandisk High Endurance I subsequently tried, along with a Transend High Endurance. Did not like the Transend, but found the Sandisk to be good sounding. Pretty close to the Exceria. Close enough that I am using the Sandisk in all my players.
The reason, for me, is due to a combination of good sound, and unbeatable price. The Sandisk High Endurance 256GB MicroSD, I can buy in HK for USD19, in a few stores, and now even a little cheaper. This is an aberration in price, as it is much more expensive everywhere. So I bought a bunch of them and am using them in everything. There are better, but nothing beats it, at this price.
For my preferences, I originally had the Sandisk Extreme Pro as the best reasonably priced card.
The Koxia Exceria, costing a bit more, replaced the Sandisk Extreme Pro. But the Exceria is not that available in stores.
My current preference is the Sandisk High Endurance, due to it's combination of Sound, Price, and better endurance
The above is my choice for affordable cards.
For "best card", price no object, that needs another list.
Sonywalkmanuser
Headphoneus Supremus
@ttt123
You may find this article interesting. Tesla MCU suffered from increased premature failures due to increased in firmware size stored on its NAND. The data logging eventually wears out the nand chip due to insufficient free space for wear leveling.
https://insideevs.com/news/376037/tesla-mcu-emmc-memory-issue/
Maybe it is a good idea to keep some free space(10%) on our microsd cards/internal storage and don’t fill it to the brim(0% free).
You may find this article interesting. Tesla MCU suffered from increased premature failures due to increased in firmware size stored on its NAND. The data logging eventually wears out the nand chip due to insufficient free space for wear leveling.
https://insideevs.com/news/376037/tesla-mcu-emmc-memory-issue/
Maybe it is a good idea to keep some free space(10%) on our microsd cards/internal storage and don’t fill it to the brim(0% free).
- Joined
- Oct 14, 2013
- Posts
- 28,361
- Likes
- 32,235
I am surprised that Tesla engineers allowed it to happen. Obviously, there should be some free spaces for the memory to conduct errors corrections and so on@ttt123
You may find this article interesting. Tesla MCU suffered from increased premature failures due to increased in firmware size stored on its NAND. The data logging eventually wears out the nand chip due to insufficient free space for wear leveling.
https://insideevs.com/news/376037/tesla-mcu-emmc-memory-issue/
Maybe it is a good idea to keep some free space(10%) on our microsd cards/internal storage and don’t fill it to the brim(0% free).
Sonywalkmanuser
Headphoneus Supremus
Maybe it was intentional? After warranty servicing is a profitable business after all?I am surprised that Tesla engineers allowed it to happen. Obviously, there should be some free spaces for the memory to conduct errors corrections and so on
andrewski
500+ Head-Fier
- Joined
- Oct 17, 2015
- Posts
- 621
- Likes
- 879
I had no idea storage had such short life spans. Would be neat to see a TBR lifespan.@ttt123, @Whitigir, @andrewski
I have gathered some data on Microsd Endurance figures, do note that these are just estimated values from the Manufacturers, actual real world TBW is dependent on operating temperatures and other variables.
Manufacturer Rated TBW for 128GB microsd cards(do take note that the MB/sec varies across vendors, but all based on sequential writes):
Sandisk High Endurance 117 TBW
Sandisk Max Endurance 702 TBW
Samsung Pro Endurance (2018) 512.4 TBW
Samsung Pro Endurance (2022) 819.9 TBW
Lexar High-Endurance 135 TBW
Kingston High-Endurance 117 TBW
ADATA High Endurance 234 TBW
Transcend High Endurance 350V 351 TBW
Kioxia Exceria High Endurance 189 TBW
Swissbit S55U 940 TBW
Micron I400 175 TBW
WD Industrial XI 384 TBW
Integral High Endurance 366 TBW
WD Purple 64 TBW
ADTEC Industrial(MLC) 313.6 TBW
Data sources:
https://www.reddit.com/r/raspberry_...bility_of_microsd_endurance_cards_compared_w/
Swissbit S55U Datasheet (only available upon private request)
Micron I400: https://www.mouser.sg/new/micron-technology/micron-i400-microsd-cards/
WD Industrial XI: https://www.avnet.com/wps/wcm/conne...-US.pdf?MOD=AJPERES&CVID=mReoKQ5&CVID=mReoKQ5
integral: https://www.integralmemory.com/product/micro-sd-card-for-dash-cam-security-cam-high-endurance/
Wd purple: https://www.amazon.com/Western-Digital-Purple-Surveillance-WDD0128G1P0C/dp/B088CD4Z1Z
ADTEC industrial: https://www.adtec.co.jp/file/industry/Datasheet_microSD_MLC.pdf
From experience, it's good to see Kingston at the bottom of the list. But I think 117 TBW is way too generous.
Sony HI-MD Minidiscs claimed 1,000,000 rewrites before degradation (1000 TBW). I'm doubting that now.
Last edited:
Sonywalkmanuser
Headphoneus Supremus
I had no idea storage had such short life spans. Would be neat to see a TBR lifespan.
From experience, it's good to see Kingston at the bottom of the list. But I think 117 TBW is way too generous.
Sony HI-MD Minidiscs claimed 1,000,000 rewrites before degradation (1000 TBW). I'm doubting that now.
TBR is actually related to TBW in this way:
Over time, the firmware algorithms will have to move frequently read data to spare blocks as that frequent read cells will eventually fail:
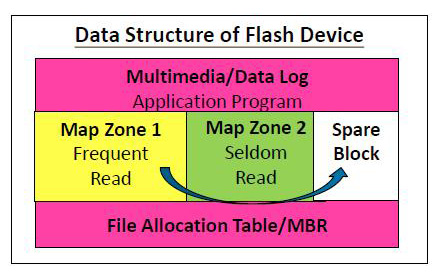
https://www.sdcard.org/press/though...-reliable-storage-in-automotive-applications/
Last edited:
Interesting article.@ttt123
You may find this article interesting. Tesla MCU suffered from increased premature failures due to increased in firmware size stored on its NAND. The data logging eventually wears out the nand chip due to insufficient free space for wear leveling.
https://insideevs.com/news/376037/tesla-mcu-emmc-memory-issue/
Maybe it is a good idea to keep some free space(10%) on our microsd cards/internal storage and don’t fill it to the brim(0% free).
Keeping some space free on any storage media feels like the right thing to do, and wear levelling is one reason. It's just a good general practice, something learned from the strange things that we run into on PC systems. I'm sure DAPs are not the same, but still feel that leaving some free space is a good general practice.
In DAPs, wear levelling is probably less critical, as most people do not do continual writes to it, and I assume the Android OS does not use the MicroSD for any background operations, like buffering, storing logs, etc.
EDIT: I see that @Sonywalkmanuser clarified that Read operations also use wear levelling.
And Tesla not fixing a known problem that was there since 2015...yes, stories like this are unfortunately too common.
https://recalls-rappels.canada.ca/e...eral-models-cpap-and-bilevel-pap-machines-and
Philips CPAP machines had defective sound insulation foam that broke down, released foam particles and toxic gas that users breathed in every night. Philips knew about the problem in 2010, and did not fix it. Finally issued a recall in 2021, and still deny they did anything wrong. The cost to health, and unecessary deaths, is paid by the millions of users that trusted them.
This is the story on that ongoing fiasco. Reading this created a deep distrust and anger for Philips, even though I was not one of their victims. But I could easily have been...
https://www.propublica.org/article/philips-kept-warnings-about-dangerous-cpaps-secret-profits-soared
Last edited:
Sonywalkmanuser
Headphoneus Supremus
Well for those who are worried about data bit rot affecting your precious music files, maybe this product would be the solution:
https://www.flexxon.com/worm/
WORM (Write Once Read Many) Memory Card
Non-erasable & Non-rewritable solution
max 128GB though and it's freaking expensive $293.00 (not sure what currency, but likely USD)
I think this can be used to hold very important data like a bit coin purse or encryption key?
https://www.flexxon.com/worm/
WORM (Write Once Read Many) Memory Card
Non-erasable & Non-rewritable solution
max 128GB though and it's freaking expensive $293.00 (not sure what currency, but likely USD)
I think this can be used to hold very important data like a bit coin purse or encryption key?
Last edited:
Sonywalkmanuser
Headphoneus Supremus
Hi, did you come to any conclusions as to what SD cards work well (I am less interested how they might sound but more on a 1 TB card working efficiently and durably (given that the advice here seems that fast read/writes are not THAT necessary) on my WM1ZM2 for a few years. Or would my current SanDisk Ultra A1 Micro XC I's version of 1TB be good enough v their Extreme version or are there recommended other ones ? Any thoughts appreciated. Thanks! N
I would think since you already have Sandisk Ultra 1TB, just use it first unless you are looking to upgrading to a bigger capacity. The Sandisk Ultra has more than sufficient read speed to handle any kind of music from the Walkman.
Sonywalkmanuser
Headphoneus Supremus
The new Samsung Pro Ultimate seems to be an interesting new microsd card, Samsung touts better error correction and more power efficiency with 28nm controller
However what worries me about Samsung from a sound quality POV is the max current consumption stated in the datasheets:
https://download.semiconductor.sams...ata_sheet_microSD_Card__PRO_Ultimate_v1.0.pdf
Swissbit S55U data sheet worse case current consumption is only 170mA for writes, 140mA for reads.(do note that the Swissbit is a slower read/write card vs the samsung)
Most other microsd cards that have listed datasheets, also typically do not exceed 400mA for max current consumption.
https://news.samsung.com/us/samsung-unveils-new-pro-ultimate-memory-cards/Increased Reliability and Durability
The Samsung PRO Ultimate provides professional photographers and creators with reliable performance, thanks to the controller’s enhanced Error Correction Code (ECC) engine and multi-proof protection features that ensure safer data storage over extended periods.
With an upgrade to the ECC’s Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) code from a 1-kilobyte (KB) to a 2KB engine, the PRO Ultimate offers enhanced durability for a higher volume of write-and-erase cycles.
The PRO Ultimate passes the industry’s most rigorous test settings and offers worry-free usage even in challenging environments, with features such as water protection for up to 72 hours in two meters of depth, drop-proof design from heights of up to five meters, wear-out protection for up to 10,000 swipes, as well as X-ray and magnetic protection. It can also operate in extreme temperatures ranging from -25°C to 85°C (-13°F to 185°F). Additionally, the PRO Ultimate SD card provides shock protection of up to 1,500g.
Maximised Power Efficiency with 28nm Controller
A new 28-nanometer (nm) controller brings a 37% improvement in power efficiency compared to Samsung’s previous lines that include the 55nm controller. This gives consumers the ability to use their devices for extended periods without the need for frequent recharging, allowing users to make the most out of their device’s battery life.
However what worries me about Samsung from a sound quality POV is the max current consumption stated in the datasheets:
2) SDR104: 1.8V Signaling, Frequency up to 208 MHz, up to 104MB/sec, Max. Current Consumption 800mA (varies by test conditions)
3) DDR200 : 1.8V Signaling, Frequency up to 208 MHz, up to 200MB/sec, Max. Current Consumption 800mA (varies by testconditions)
https://download.semiconductor.sams...ata_sheet_microSD_Card__PRO_Ultimate_v1.0.pdf
Swissbit S55U data sheet worse case current consumption is only 170mA for writes, 140mA for reads.(do note that the Swissbit is a slower read/write card vs the samsung)
Most other microsd cards that have listed datasheets, also typically do not exceed 400mA for max current consumption.
Last edited:
Sonywalkmanuser
Headphoneus Supremus
@andrewski
If you are interested in building a dedicated audiophile PC for audio ripping/playback, here's something interesting from Sony's mad audio engineer, according to him, the chassis contruction and material of the PC matters for sound quality too!(yup, shocking right?):
http://kanaimaru.com/pc5_yakipaso/pc5-7.htm
Maybe the Aluminium chassis on the WM1AM2 helps to produce clean sound too.
If you are interested in building a dedicated audiophile PC for audio ripping/playback, here's something interesting from Sony's mad audio engineer, according to him, the chassis contruction and material of the PC matters for sound quality too!(yup, shocking right?):
Case (chassis) sound quality
This time it's mechanical again, and the sound quality of the case (chassis). In the case of a PC, it is generally called a ``case'' because it includes a power supply, but from an audio standpoint, it is just a chassis, and it is important for sound quality.
1. Why the chassis is important
There are at least two fans inside the PC, even if there is no sound coming from the speakers. Power supply fan and CPU cooler. When considering sound quality, lowering the rotation speed of the fans to the extent that there is room for temperature rise will improve the sound quality, but vibrations will still remain.
The CPU fan can also be made fanless by using water cooling or a large heat sink. However, it is usually safer to turn on the fan. Reason,
That's about it. 3 is surprisingly a blind spot and one of the drawbacks of the water cooling system.
There are still some sources of vibration inside the chassis. The most harmful thing is the vibration noise of the CD-R (same as DVD/BD) drive.
When it comes to CD drive vibrations, most people tend to focus on the vibrations of the rotary drive motor, but in reality, the frequency is low (a few tens of Hz at most), so it's not that harmful. The troublesome part is actually the optical system.
The optical system uses a focus servo and a tracking servo to track the lens to the CD surface, but the driven lens is quite heavy. The impedance of the drive coil is around 8Ω, so it is exactly like a speaker, but when viewed as a vibration system, the lens is much heavier than the tweeter, and the drive power is light, around 1 watt. The frequency is also up to about 1kHz. In other words, it is a considerable source of vibration.
If the chassis is not properly balanced, these sources of vibration will quickly be transmitted to the circuit components, modulating the audio signal and the clock used to create the audio signal, which will affect the sound quality.
Kanamaru is originally an amplifier designer, but as you know, he is also a CD player designer. The first CD player we designed was the CDP-R1, which won the Golden Sound Award from Stereo Sound magazine. While designing this, I realized that when audio equipment has a rotating system, its sound quality responds very sensitively to the performance of the chassis.
If you use it in a place that receives the sound pressure of a speaker, you can easily imagine that vibrations caused by the sound pressure of the speaker will occur in the chassis, causing a reaction in the servo system. But apparently that's not all. It seems that the quality of the chassis changes the sound quality even when there is no sound pressure.
So, when I changed the parts and structure of the machine in a silent state with no sound emitted from the speakers, and recorded the sound on a cassette each time, I listened to it all together later, and the sound quality changed quite a bit. What I realized is that regularly occurring mechanical noise modulates the contact resistance of components and contacts in the signal path, and for example, the frequency characteristics of this modulate the sound quality or make it unpleasant. .
The reason for the frequency characteristics is, for example, if we consider the vibration of the optical system as a starting point, that vibration is transmitted to the chassis. The chassis has several resonant frequencies, and the vibration level increases at those frequencies. This vibration is transmitted to the drive and changes the position of the optical spot. The optical system then operates to eliminate spot misalignment. This action is a kick to the optics, so the reaction is transmitted to the chassis. The loop is now complete. In the end, you can think of it like this: the resonance mode of the chassis is amplified through the optical system, and the quirks are emphasized. This is why it is so difficult to design the sound quality of drives such as CD players, but this is one of the key points in taking care of the sound quality of your PC.
In addition, the drive current of the optical system is quite large, and the magnetic circuit of the drive coil is generally open, so the lines of magnetic force caused by the drive current leak from the drive. These magnetic lines of force strongly reflect vibrations, so if they are even slightly inserted into other circuits (for example, clock systems), the sound quality will be immediately affected.
This change in sound quality can be seen even with headphones. However, in the end, the way the space is created when playing through speakers is quite important, and this is difficult to discern with headphones. Even if you can understand the tone, it is difficult to judge the spatial reproduction created by the speakers using headphones. The method of recording onto cassettes was devised to solve this problem, and this is also the reason why Kanimaru burns CD-Rs to check the sound quality on a PC.
The ``recording method'' is a sound quality tuning method devised by Kanamaru, but there is also a method for making similar judgments called the adjoining room method. The target device is placed in a silent adjacent room, and vibrations are blocked to judge the sound quality. However, it is difficult to create an "adjacent room" facility, and it requires a large remote control or an assistant, so I think it is rare that even professionals use it.
2. Simple cases are best.
Let me introduce some empirical principles. First of all, the simpler the structure of the chassis, the better the sound quality.
Almost all high-quality homemade cases can be pulled out with the motherboard attached. This means that the chassis is complicated, and the structure is actually very problematic in terms of vibration. When you try tapping on the case, many of them make an unpleasant crunching noise. I'm not saying that the removable structure is bad, but at least the condition is that it makes a clear "concon" sound no matter where you hit it.
However, it is no match for something with a simple structure. Generally speaking, such products are only available on cheap products with reduced costs, and they tend to have thin steel plates that are ``insufficient in strength'' and tend to produce a cheap sound.
That's why Kanimaru pays close attention to the chassis that come up at auctions, and when he finds something simple, he sometimes bids on it and listens to the sound. I avoid expensive things and only buy things that cost less than 2,000 yen, but there are some pretty good ones out there. When walking around Akihabara, you'll also notice junk chassis.
This is a recent hit. Judging from the exhibited images, it looks simple and durable. The low price of 500 yen without a power supply is also attractive. I placed a bid and was successful. The shipping cost was more than double.
The best part about this case is that the motherboard mounting part is made from an embossed iron plate, rather than the typical brass or iron hex boss.
In fact, the "screw-in boss" that is often found in homemade cases is not good in terms of sound quality. First of all, I have a problem with it coming loose after I use it. If you tighten it too tightly, the screw may break. Brass bosses in particular tend to make noise and have a peculiar sound quality, so they are usually avoided in audio design. Even if a boss is used, caulking or welding, which is common in manufacturer's PCs, is OK. As for the material, galvanized iron (combined with chromate) is good.
But the drawing process is better than any boss. This is actually the first time I've ever gotten my hands on a drawn PC case, but when I tried to attach the board to the chassis so that it stuck to the chassis and hit the board, it sounded really nice. The sound quality was also very good.
Apart from this part, the overall structure of this case was simple, and it was wonderful with no looseness anywhere. It's definitely a case that sells separately, but I'm sure it's cheap. However, it was a good product that was difficult to obtain.
3.Is it iron or aluminum?
The case above is made of iron. When comparing aluminum and steel, iron has a stronger sound. In the case of iron, the chassis impedance is slightly higher, but drawing processing is advantageous in that respect as well.
So what about aluminum cases? Aluminum generally produces a clean sound with less dirt. However, it is best to avoid cheap aluminum plates that are thin. It tends to sound really cheap. Of course, if the board is thick enough, the sound quality tends to be good, and in that case, it has a characteristic different from iron. After all, an aluminum chassis should be about 2mm thick (although there are exceptions), and improving sound quality costs money.
Well-made ones with iron chassis are cheap and have good sound. It is difficult to bring out the best qualities of aluminum, but let's say that it has the ultimate characteristics that you can spend money on.
http://kanaimaru.com/pc5_yakipaso/pc5-7.htm
Maybe the Aluminium chassis on the WM1AM2 helps to produce clean sound too.
Last edited:
Sonywalkmanuser
Headphoneus Supremus
@ttt123 @Whitigir
I think this is interesting information for modding audio equipment: Use of Teflon tape to dampen vibration from heatsinks:
http://kanaimaru.com/pc5_yakipaso/pc5-5.htm
Also high-end PC heatsinks(with thin fins) do not sound good according to him
I think this is interesting information for modding audio equipment: Use of Teflon tape to dampen vibration from heatsinks:
1.CPU cooler (CPU fan + heatsink) is an important component for sound quality, but...
In the world of amplifiers, the type of heatsink you use, from the large ones used in power amps to the small ones on the board, has an impact on the sound quality. This is important. The amplifiers and CD players designed by Kanamaru have carefully selected heat sinks, and are tuned using Teflon tape to lightly dampen vibrations.
This is a heat sink for the power amplifier of an AV amplifier, but there is a rib in the middle of the fin, and the position of the rib is shifted on all the fins. No two fins have ribs in the same position. This is to suppress resonance by changing the resonant frequency of each fin. Also, what you can see faintly on the edge of the fin is Teflon tape. This also stops the fins from squealing.
In the case of a PC, it may be impossible to use parts that have been tuned to this level (because they don't exist in the first place), but a little knowledge can make a huge difference in sound quality.
http://kanaimaru.com/pc5_yakipaso/pc5-5.htm
Also high-end PC heatsinks(with thin fins) do not sound good according to him
3. What is a CPU cooler that makes a bad sound
? So, what kind of cooler is a bad sound?
High-end and expensive products generally have poor sound, but one that is especially bad is "precision thin fins."

For example, this atmosphere. By the way, this image is a composite image and is not the actual product.
There is a fan on the other side where you can't see it. With forced air cooling, if the volume is the same, the larger the surface area, the cooler it will be, so it is advantageous to use a large number of thin fins, which is why this happens.
However, according to common sense in amplifier design, this type of fin does not produce good sound. Each aluminum plate is too thin and vibrates in parts, making a ``chattering'' sound, resulting in a very bad sound quality in the mid-high range. Since it is cheap in terms of cost, it is sometimes used in low-priced amplifiers, but in such cases it is also used in conjunction with anti-vibration processing to improve sound quality. Don't use it unprotected like a CPU cooler.
The extrusion method tends to produce good sound quality because it does not produce a crackling sound.
Ah, don't you know what "extrusion manufacturing method" means? I'm sure you'll understand if I give you another example.
4.Aluminum extrusion manufacturing method

This is a typical extrusion heat sink. Molten aluminum is placed in a mold and the aluminum is extruded through the holes drilled in the mold. The holes are in the shape of comb teeth, and first a long aluminum sash with the same shape as Kintaro candy is made. Cut it to size and it will become a heat sink. In other words, the surface you can see in the image is the one that was cut, and the recessed part at the bottom is created by cutting and then further machining.
The part that touches the CPU is a thick base, and the fins that extend upward from it are made of the same continuous metal. Since the thick fins are integrated with the base, split vibrations are less likely to occur and the sound quality is good.
High-end PU coolers are made of heat pipes, copper, and precision thin fins, but they do not have good sound quality. No one compares them, so things like that are probably praised, but heat sinks are cheap and simple, made only from extruded aluminum, and have high sound quality.
Last edited:
Sonywalkmanuser
Headphoneus Supremus
His Usb cable recommendation: Supra
http://kanaimaru.com/NWA840/009.htm
His Lan cable recommendation: SAEC SLA-500
http://kanaimaru.com/NWA840/008.htm
LAN terminal for better sound:
http://kanaimaru.com/NWA840/005.htm
How to make your own power cord(for DIY experts only):
http://kanaimaru.com/NWA840/011.htm
http://kanaimaru.com/NWA840/012.htm
http://kanaimaru.com/NWA840/013.htm
http://kanaimaru.com/NWA840/014.htm
http://kanaimaru.com/NWA840/015.htm
http://kanaimaru.com/NWA840/016.htm
http://kanaimaru.com/NWA840/017.htm
http://kanaimaru.com/NWA840/018.htm
http://kanaimaru.com/NWA840/019.htm
http://kanaimaru.com/NWA840/020.htm
how to make a Kanamaru type non-resonant rack:
http://kanaimaru.com/NWA840/002.htm
http://kanaimaru.com/NWA840/003.htm
http://kanaimaru.com/NWA840/009.htm
His Lan cable recommendation: SAEC SLA-500
http://kanaimaru.com/NWA840/008.htm
LAN terminal for better sound:
http://kanaimaru.com/NWA840/005.htm
How to make your own power cord(for DIY experts only):
http://kanaimaru.com/NWA840/011.htm
http://kanaimaru.com/NWA840/012.htm
http://kanaimaru.com/NWA840/013.htm
http://kanaimaru.com/NWA840/014.htm
http://kanaimaru.com/NWA840/015.htm
http://kanaimaru.com/NWA840/016.htm
http://kanaimaru.com/NWA840/017.htm
http://kanaimaru.com/NWA840/018.htm
http://kanaimaru.com/NWA840/019.htm
http://kanaimaru.com/NWA840/020.htm
how to make a Kanamaru type non-resonant rack:
http://kanaimaru.com/NWA840/002.htm
http://kanaimaru.com/NWA840/003.htm
Last edited:
Users who are viewing this thread
Total: 24 (members: 4, guests: 20)






















